
A little crab
is enough to change the world

is enough to change the world
Chitin, which is widely found in shrimp and crab shells, is a polysaccharide made by the polymerization of N acetyl glucosamine.
Chitin is deacetylated to obtain chitosan.
In the past ten years, the research on chitin and chitosan has been widely carried out at home and abroad, and their functions in anti-tumor and prevention and treatment of pathogenic microorganisms have attracted more and more attention. However, due to its insoluble water, it is very limited in the development of applications. To this end, chitosan is degraded into Chito-oligosaccharides (also known as oligosaccharides, chitosan oligosaccharides, chitosan oligosaccharides) by appropriate methods, that is, oligosaccharides composed of 2~10 aminoglycoses linked by β-1-4 glycosidic bonds.
Through a series of experiments, it has been found that it not only has good water solubility, is easy to be absorbed by the human body, but also has a variety of physiological functions such as antibacterial, anti-tumor, blood lipid regulation, immune regulation and activation of intestinal bifidobacteria, and the application field has been greatly broadened.
Chito-oligosaccharides has a unique application value in fine chemicals, biomedicine, health food, agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry.
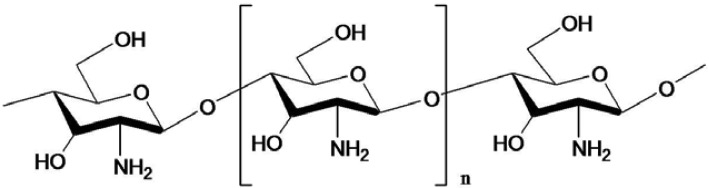
Chito-oligosaccharides chemical structure
Chito-oligosaccharides is a multifunctional biopolymer derived from chitin that has been widely used in several industries due to its unique properties. This biodegradable and non-toxic compound offers a range of advantages in various areas:

Chitosan has a variety of benefits and functions in agriculture. Here's an overview:
The optimal dosage of chitosan can vary greatly depending on the type of crop, the intended purpose (such as growth promotion or pest control), and the specific formulation of the product.
For best results, farmers and growers are advised to consult with an agricultural expert or extension service, tailored to their specific crop and local conditions. It is also important to follow the manufacturer's instructions for the chitosan products used.
In agriculture, chitosan is often used in various forms to take advantage of its beneficial properties. Each form of chitosan used in agriculture has different benefits, functions, and recommended dosages that are tailored to specific agricultural applications. These include:
Benefits: Protects against fungal, bacterial, and viral infections; Get rid of pests.
Function: Stimulates plant defense mechanisms when applied to leaves.
Dosage: Generally used at a concentration of 0.1-1.0%. The frequency and quantity depend on the type of crop and the pressure from pests and diseases.
Advantages: Improves germination rate, early seedling growth, and provides initial disease protection.
Function: Seeds are coated to enhance growth and immunity.
Dosage: Chitosan concentrations in seed coating solutions are typically 0.5-1.5%. Use as a coating before sowing.
Benefits: Improves soil quality, increases water retention, and promotes root growth.
Function: Mixes with soil to improve its structure and microbial activity.
Dosage: Varies depending on soil type and conditions, and is usually applied at the beginning of the crop cycle or as needed.
Benefits: Improves nutrient uptake efficiency; Enhance soil health.
Function: Incorporating into fertilizers to improve their efficacy.
Dosage: Usually a small fraction of the overall fertilizer composition; The exact proportion depends on the type of fertilizer and the needs of the crop.
Benefits: Provide targeted nutrient or pesticide delivery for increased efficiency.
Function: Used for precise application to plants, minimizing waste.
Dosage: highly specific and based on target needs; Due to its high efficiency, it is usually used in the least quantities.
These forms are chosen based on specific needs, such as improving plant health, preventing pests, or increasing crop yields. Each form makes use of Properties of chitosan, such as biodegradability, non-toxicity, and the ability to enhance plant immunity and growth. At the same time, each form of chitosan application is designed to leverage its unique properties to improve crop health and yields, contributing to sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
When considering the use of chitosan in agriculture, the choice between acid-soluble chitosan, chitosan hydrochloride, and Chito-oligosaccharides depends on several factors, including specific agricultural application, effectiveness, ease of use, and crop safety. Each type has its own unique features and benefits:
Properties: Soluble in acidic solutions, usually derived from the deacetylation of chitin.
usages : commonly used for its antifungal properties and growth stimulants.
Advantages: Effectively enhance plant immunity and increase yield.
Precautions: Acidity can be an issue for certain soil types or crops.
Properties: Chitosan in hydrochloride form, known for its water solubility.
usages : Commonly used for foliar applications and as a seed treatment.
Advantages: Better solubility in water, making it easier to apply and generally effective in promoting seed germination and plant growth.
Precautions: It is important to carefully manage concentrations to avoid potential plant toxicity.
Properties: Consists of short polymer chains, enhancing its solubility and biological activity.
usages : Widely used for its biostimulant and biopesticides properties.
Advantages: High biological activity means that it is effective at lower concentrations, and its smaller molecular size is more easily absorbed by plants.
Notes: May be more expensive due to the processing required to break down chitosan into oligosaccharides.
Specific agricultural needs: The choice depends on what you're trying to achieve, for example, disease control, growth stimulation, or improving resilience to stress.
Crop safety: Each type may interact differently with different crops, so it's important to consider crop tolerance.
Environmental conditions: Soil pH, climate, and other environmental factors can affect the effectiveness of different chitosan types.
Application method: The ease of application (e.g., foliar sprays, soil amendments) and the concentration level required may vary depending on the type.
Cost-effectiveness: Consider the cost of advantages and effectiveness over a specific use case.
Regulatory compliance: Ensure that the type selected complies with local agricultural regulations.
recommendedIt is often recommended to conduct trials or refer to crop- and region-specific agricultural studies to determine the most effective type of chitosan. Consulting with an agricultural expert or extension service can also provide valuable guidance based on your specific conditions and requirements.
Yes, there have been several successful trials and studies that have demonstrated the effectiveness of chitosan in agriculture. These studies cover all aspects of agricultural applications, including plant growth promotion, disease resistance, pest and disease control, and improving crop yield and quality. Here are some of the key highlights:
These trials and studies have been conducted in different geographical locations and on a variety of crops, highlighting the versatility and wide range of benefits of chitosan in agriculture. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of chitosan can vary depending on factors such as its concentration, molecular weight, source, and specific crop and environmental conditions. Ongoing research and field trials help to optimize its use and understand its full potential in sustainable agriculture.
Chitosan is derived from crab shells and is emerging as a sustainable alternative in agricultural practices. Its benefits in agriculture are manifold, including stimulating plant growth, increasing yields, enhancing disease resistance, and acting as a natural deterrent to pests.
Chitosan can increase seed germination rates, improve plant stress resistance, and help improve soil health. Its applications range from Biopesticides and Biostimulants to Soil amendments and seed treatments. The effectiveness of chitosan can vary depending on factors such as its molecular structure, crop type, and environmental conditions. Being eco-friendly and sustainable, it provides a viable option for those looking for eco-conscious agricultural solutions. Chitosan is expected to develop in future agricultural development due to its crab shell source and biodegradability.
The service has a warm connection with the customer