
A little crab
is enough to change the world

is enough to change the world
Chitin, which is widely found in shrimp and crab shells, is a polysaccharide made by the polymerization of N acetyl glucosamine.
Chitin is deacetylated to obtain chitosan.
In the past ten years, the research on chitin and chitosan has been widely carried out at home and abroad, and their functions in anti-tumor and prevention and treatment of pathogenic microorganisms have attracted more and more attention. However, due to its insoluble water, it is very limited in the development of applications. To this end, chitosan is degraded into Chito-oligosaccharides (also known as oligosaccharides, chitosan oligosaccharides, chitosan oligosaccharides) by appropriate methods, that is, oligosaccharides composed of 2~10 aminoglycoses linked by β-1-4 glycosidic bonds.
Through a series of experiments, it has been found that it not only has good water solubility, is easy to be absorbed by the human body, but also has a variety of physiological functions such as antibacterial, anti-tumor, blood lipid regulation, immune regulation and activation of intestinal bifidobacteria, and the application field has been greatly broadened.
Chito-oligosaccharides has a unique application value in fine chemicals, biomedicine, health food, agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry.
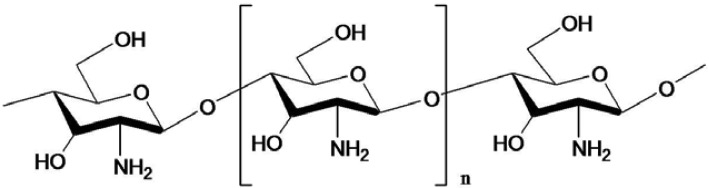
Chito-oligosaccharides chemical structure

2.1 Biological activity. Chito-oligosaccharides has a water solubility of more than 99% and a human absorption rate of 99.88%, which has superior biological activity than chitosan. It can improve the flora distribution of intestinal microbes, stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria, and its pharmacological activity is 14 times that of chitosan of the same weight. Experiments have shown that Chito-oligosaccharides can proliferate Bifidobacterium by 120 times when applied to dairy products.
2. 2 Antibacterial and antibacterial effect. Chito-oligosaccharides has a pronounced antibacterial and antibacterial effect. Its antibacterial effect is also gradually enhanced with the decrease of the molecular weight of Chito-oligosaccharides, with a molecular weight of 1 814, the degree of deacetylation of 84% Chito-oligosaccharides treated non-woven fabrics, it was found that the concentration of 0.01% against Proteus vulgaris reached 90%, while for Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, 0.05%, the molecular weight is 2 000~ 30 000, and the degree of deacetylation is 91.5% Chito-oligosaccharides inactivates two oral pathogens, Actinobacillus actinobacillus and Streptococcus mutans.
2. 3 Anti-tumor effects. Chito-oligosaccharides can improve the body's immune activity and anti-cancer ability, and has a significant inhibitory effect on liver cancer cells.
2. 4 Disease prevention and disease resistance of plants. Chito-oligosaccharides also acts as a plant regulator to enhance the plant's defenses against pests and diseases. Oligosaccharides have the functions of regulating plant growth, development, reproduction, disease prevention and resistance, etc., can stimulate the immune system response of plants, activate defense responses, produce active substances with disease resistance, and inhibit the formation of diseases.
Chito-oligosaccharides, derived from marine crab shells, provide several benefits and functions when applied to textiles:
Benefits of Chito-oligosaccharides in textiles:
Biodegradability: Chito-oligosaccharides are natural biopolymers that provide an ecologically sound alternative to synthetic reagents. Its biodegradable properties help reduce environmental impact, in line with sustainable textile manufacturing practices.
Eco-friendly dyeing process: Chitosan is used as a natural mordant in the dyeing process, helping to reduce reliance on harsh chemical mordants, thereby reducing environmental pollutants and improving the sustainability of the dyeing process.
Green Footprint: The use of Chito-oligosaccharides helps to reduce the overall ecological footprint of textile production, supporting the industry's shift towards greener and more responsible manufacturing methods.
Non-toxic: Unlike many chemical additives, Chito-oligosaccharides are non-toxic and can therefore be safely used in a wide range of textile applications, including those that come into close contact with the skin.
Biocompatibility: Its inherent biocompatibility makes it particularly valuable in medical textiles, where it has the least risk of skin irritation or allergic reactions, which is a key factor in healthcare-related fabric applications.
The role of Chito-oligosaccharides in textiles:
Antimicrobial properties: The antimicrobial properties of chitosan are crucial in inhibiting microbial growth, making it ideal for hygiene-critical applications such as medical textiles, sportswear, and underwear. This feature is essential for maintaining hygienic conditions and preventing odor build-up in fabrics.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability: Its moisture absorption ability enhances the breathability and comfort of the fabric, especially in apparel textiles, where humidity control is essential for the wearer's comfort.
Strength and durability: The addition of chitosan can improve the mechanical strength and durability of textiles, thereby extending the life and abrasion resistance of fabrics.
UV protection: Chitosan-treated textiles protect against harmful UV rays, adding an extra layer of protection, which is especially beneficial in outdoor and sun-exposed clothing.
Wound healing (medical textiles): Chitosan uses its wound healing ability and is of immeasurable value in medical textiles to promote the healing process of wound dressings and other medical fabrics.
Odor resistance: Reduces odors in textiles, making them more comfortable to wear.
Water treatment: In addition to traditional textiles, chitosan-coated fabrics can be used for innovative water treatment applications, leveraging their ability to bind to heavy metals and contaminants, providing a new method of water purification.
Flame retardancy: The addition of chitosan imparts flame retardant properties to textiles, which is an essential function for safety in a variety of applications, including upholstery, curtains, and protective clothing.
Antistatic: In synthetic fibers, chitosan helps to reduce static build-up and improve the comfort and usability of a variety of textile products.
In conclusion, Chito-oligosaccharides play a multifaceted role in the textile industry. Its benefits extend from enhanced environmental sustainability and safety to improved functional properties of the fabric. Its versatility and eco-friendly properties make it an increasingly popular choice for the ever-evolving textile technology and sustainable practices.
The service has a warm connection with the customer