
A little crab
is enough to change the world

is enough to change the world
Chitin, which is widely found in shrimp and crab shells, is a polysaccharide made by the polymerization of N acetyl glucosamine.
Chitin is deacetylated to obtain chitosan.
In the past ten years, the research on chitin and chitosan has been widely carried out at home and abroad, and their functions in anti-tumor and prevention and treatment of pathogenic microorganisms have attracted more and more attention. However, due to its insoluble water, it is very limited in the development of applications. To this end, chitosan is degraded into Chito-oligosaccharides (also known as oligosaccharides, chitosan oligosaccharides, chitosan oligosaccharides) by appropriate methods, that is, oligosaccharides composed of 2~10 aminoglycoses linked by β-1-4 glycosidic bonds.
Through a series of experiments, it has been found that it not only has good water solubility, is easy to be absorbed by the human body, but also has a variety of physiological functions such as antibacterial, anti-tumor, blood lipid regulation, immune regulation and activation of intestinal bifidobacteria, and the application field has been greatly broadened.
Chito-oligosaccharides has a unique application value in fine chemicals, biomedicine, health food, agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry.
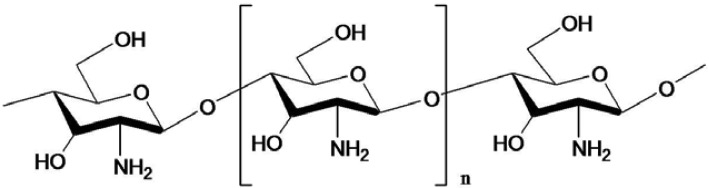
Chito-oligosaccharides chemical structure
Chito-oligosaccharides is a multifunctional biopolymer derived from chitin that has been widely used in several industries due to its unique properties. This biodegradable and non-toxic compound offers a range of advantages in various areas:

Chitosan is a chitin derivative that is becoming increasingly popular in pharmaceutical formulations due to its unique properties and benefits. The following are the application areas, advantages, functions, and typical dosages of pharmaceutical formulations:
1.Drug delivery system: due to its biocompatibility and biodegradability, it is used for controlled-release formulations.
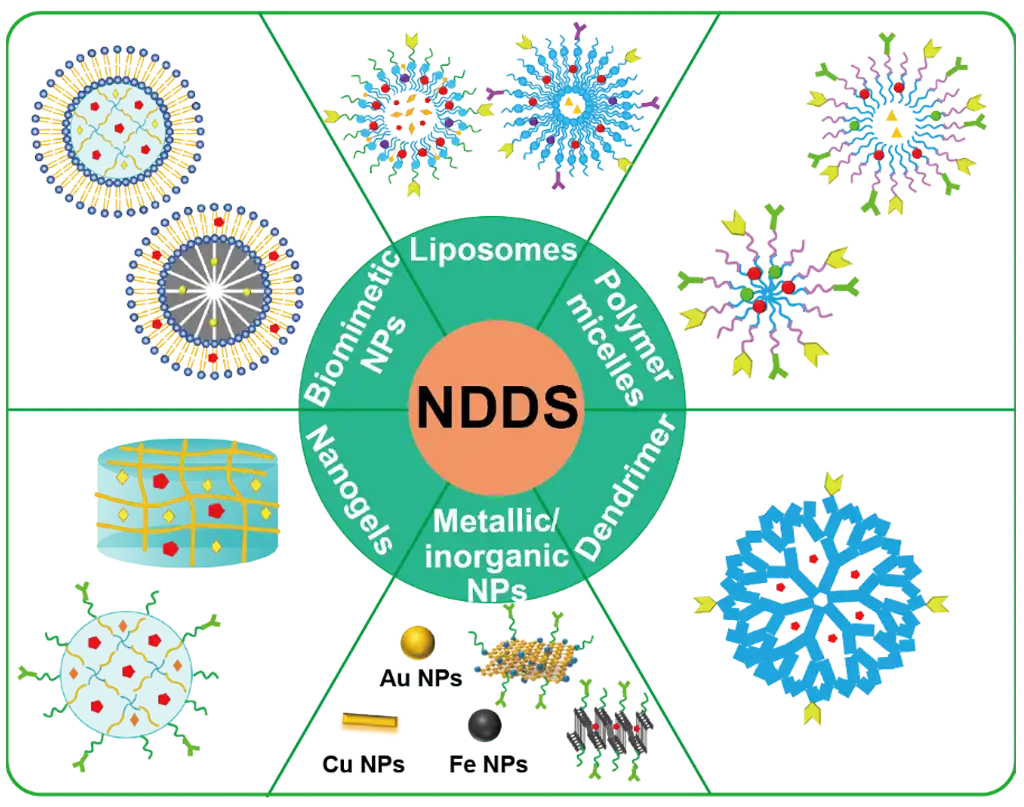
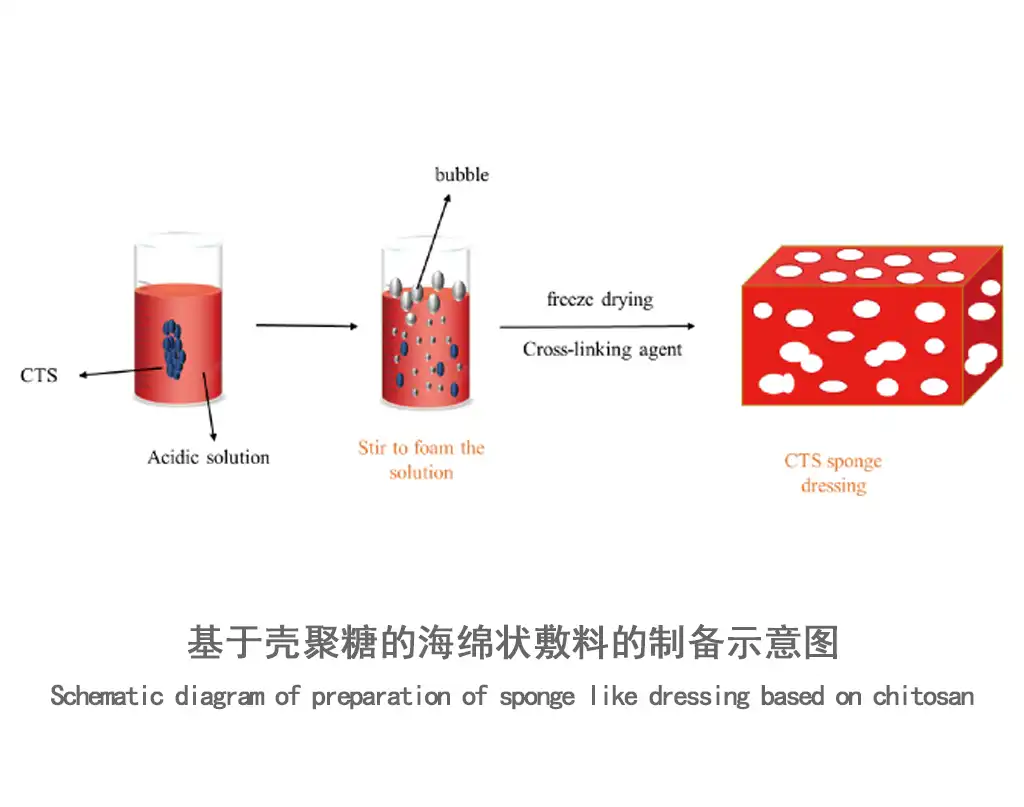
2.Wound healing: due to its hemostatic and antibacterial properties, it is implemented in dressings, gels, bandages, and other forms.
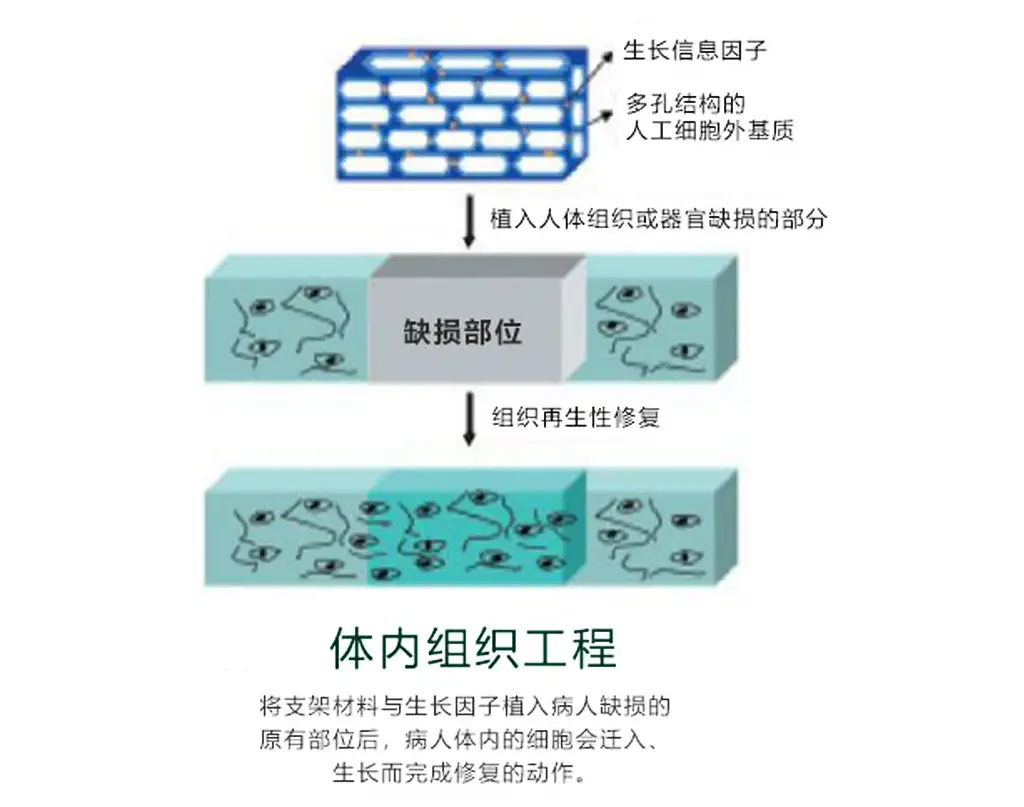
3.Tissue engineering: scaffolds that can be used for tissue regeneration.
4.Weight Management Supplements: Commonly found in products designed to lower cholesterol and aid weight loss.
Chito-oligosaccharides is highly biocompatible, meaning it is well tolerated by the human body and is biodegradable, allowing it to decompose naturally without harmful residues.
It exhibits significant antimicrobial properties against a wide range of pathogens at very low molecular weights (3kDa) and very high degrees of deacetylation (>98%), which makes it valuable in wound dressings and pharmaceutical preservatives.

Due to its mucosal adhesion properties, Chito-oligosaccharides can enhance the absorption of certain medications, especially those administered orally or topically.

In dietary supplements, it has been shown to bind to lipids in the gastrointestinal tract and may help with cholesterol management.
Its hemostatic (hemostatic ability) and antimicrobial properties make it an excellent ingredient in wound healing products.
its ability to form gels, films, and nanoparticles makes it a versatile agent in controlled-release drug formulations.
for scaffolds, using their biocompatibility to support tissue growth and regeneration.
as a dressing ingredient, it promotes healing and reduces the risk of infection.
it acts as a binder in tablet formulations, enhancing structural integrity without compromising drug release.
exploited for its potential to bind fats in the digestive system, reducing its absorption.
typically 500 mg to 3ooo mg per day, depending on the application (e.g., weight management, cholesterol lowering).
concentrations can vary greatly, but as a rule, it is used in creams or gels for skin applications by 1-2%.
concentrations vary widely depending on the type of dressing and specific wound care requirements.
dose and concentration depend on the nature of the drug, the desired release curve, and the route of administration.

Chito-oligosaccharides Its efficacy and safety should always be verified through clinical trials.
The use of Chito-oligosaccharides must comply with regulatory standards, which may vary by region and application.
response to Chito-oligosaccharides may vary depending on individual health status, age, and other factors, emphasizing the need for individualized dosage recommendations, especially in the treatment setting.
Chito-oligosaccharides is a multifaceted and promising natural ingredient in the pharmaceutical industry. Its applications are varied, from drug delivery systems to wound care, with dosages and formulations tailored to each specific usages. As research continues, we expect a wider range of applications and a deeper understanding of their potential.
there are several potential areas of chitosan function in drugs that could be further investigated:
research and development in these areas may take advantage of the unique properties of Chito-oligosaccharides to address unmet needs in medical and drug delivery, opening up new possibilities in the pharmaceutical and biomedical fields.
One of the important usages of Chito-oligosaccharides in biomedicine is the use of its antitumor effects to prepare anticancer agents. Chito-oligosaccharides, especially oligosaccharides with 6~8 sugars, can achieve anti-cancer effects by activating lymphocytes in the human body and inhibiting the reproduction and spread of cancer cells. The formation of cancer cells is accompanied by the release of a large number of cancer toxins. This poison Chito-oligosaccharides can reduce iron in the human body, causing anemia and loss of appetite, while the small molecule groups formed by Chito-oligosaccharides in the human intestine are easily absorbed by the intestines, thereby inhibiting the release of cancer toxins in the body. At the same time, Chito-oligosaccharides, as a good polyelectrolyte, can be adsorbed on the surface of blood vessel wall cells, thereby inhibiting the metastasis of cancer cells.
At present, the functions of chitin and chitosan in regulating blood lipids and lowering cholesterol have been reported. Because these polysaccharides are non-toxic, do not produce allergic reactions, and have a very mild immunostimulatory effect on the body, they have advantages in being used as blood lipid regulating and cholesterol-lowering drugs.
According to the China Industrial Development Research Center, the United States, as the birthplace of international biopharmaceuticals, is at the leading level in terms of capital investment, product development and production, and the biomedical products developed account for more than 90% of the world's total. The U.S. FDA has approved more than 100 biologic drugs, including Chito-oligosaccharides.
In 2005, the total output value of China's pharmaceutical biotechnology industry will reach 40 billion ~ 50 billion yuan, and the total output value will reach 110 billion ~ 130 billion yuan by 2015. The Ministry of Technology has designated the "Chito-oligosaccharides new product development application" as a national government The "Tenth Five-Year Plan" requires the establishment of several Chito-oligosaccharides production lines with an annual output of more than 500 tons to meet the needs of the domestic market. As a new pharmaceutical product with a certain foresight, Chito-oligosaccharides has broad prospects for domestic and foreign markets.
Chito-oligosaccharides stands out in the pharmaceutical industry for its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and non-animal origin, making it a safe and viable ingredient in a variety of medical applications. Its antimicrobial properties are essential for reducing the risk of infection, especially in wound care, while its ability to enhance drug absorption can significantly improve treatment outcomes, especially in oral and transdermal delivery systems.
Functionally, Chito-oligosaccharides play a key role in controlled drug delivery, thanks to its gel-forming capabilities and customizable drug extended-release capabilities. Its mucoadhesion properties enhance the effectiveness of the drug on mucosal surfaces, and its role in tissue engineering and wound management is marked by its support structure and healing properties. This versatility makes Chito-oligosaccharides a key ingredient in advancing pharmaceutical technologies and therapeutics.
The service has a warm connection with the customer